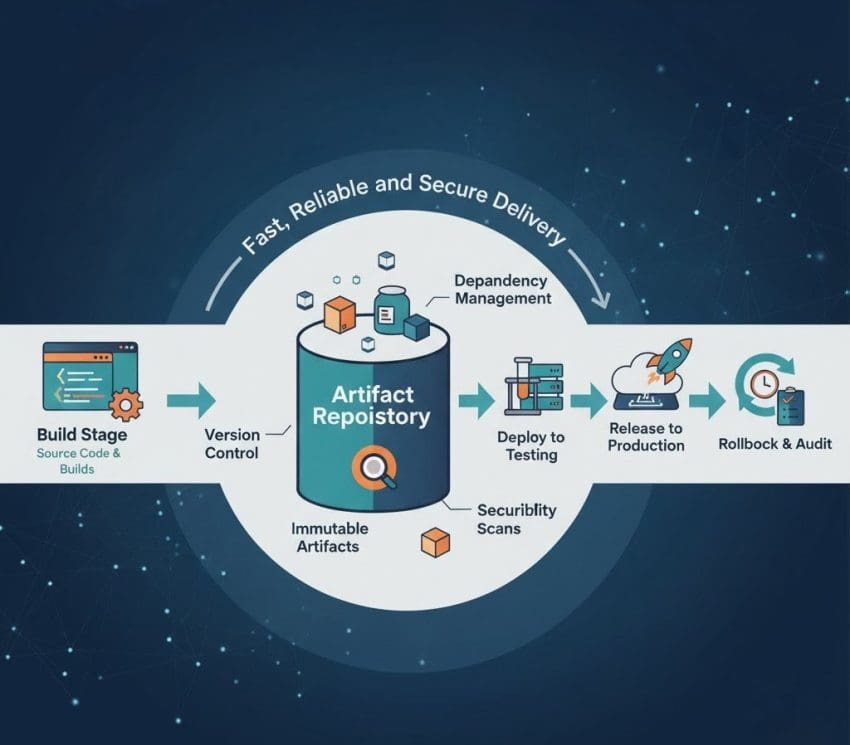
When working with Java-based projects, source code isn’t directly deployed, it first needs to be packaged into build artifacts such as .jar, .war, or .ear files. Once these artifacts are created, they are stored in a centralized artifact repository, ensuring version control, collaboration, and consistency across environments.
📁 Purpose of an Artifact Repository
An artifact repository acts as a central hub for all generated build artifacts. For instance, a developer may need to access an older version of a .jar file created months or even years ago. Instead of rebuilding the entire project or setting up containers, they can simply download the required artifact from the repository and run it locally.
This approach provides:
- Easy access to multiple versions of artifacts
- Reliable rollback capabilities
- Better traceability across builds
🧩 Dependency Management and Approved Packages
Organizations often maintain a strict policy where developers can only use approved or verified dependencies. To enforce this, all required .jar files or third-party libraries are stored in the artifact repository.
When developers include these dependencies in their projects, tools like Maven can automatically fetch them from the repository instead of external sources. The repository location is defined in the project’s pom.xml file.
Example configuration:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>company-artifacts</id>
<url>https://artifacts.company.com/repository/maven-releases/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>This ensures that all teams use consistent and secure dependencies across different projects.
🧱 Commonly Used Artifact Repositories
Several artifact repositories are widely adopted across DevOps environments:
- JFrog Artifactory 🧪 – A popular, enterprise-grade repository supporting multiple formats including Maven, npm, Docker, and Helm.
- Sonatype Nexus Repository 🧰 – A widely used, open-source repository manager known for handling both public and private components efficiently.
- AWS CodeArtifact ☁️ – A fully managed artifact repository service integrated with AWS services and CI/CD workflows.
- GitHub Packages 🐙 – Useful for storing versioned artifacts within GitHub-hosted projects.
These repositories integrate seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines and build tools, making artifact management smoother and more secure.
🧠 Summary
Artifact repositories serve as the warehouse for build outputs and dependencies.
They help teams:
✅ Store and version .jar, .war, or .ear files
✅ Reuse and share artifacts across multiple projects
✅ Control and verify dependencies
✅ Improve CI/CD integration and traceability
🎯 Wrapping It Up
Without artifact repositories, managing builds and dependencies across large projects would become time-consuming and error-prone. Tools like JFrog Artifactory, Sonatype Nexus, and AWS CodeArtifact make artifact management organized, secure, and scalable, forming a core part of any modern DevOps pipeline.
To dive deeper… Check out these related topics: