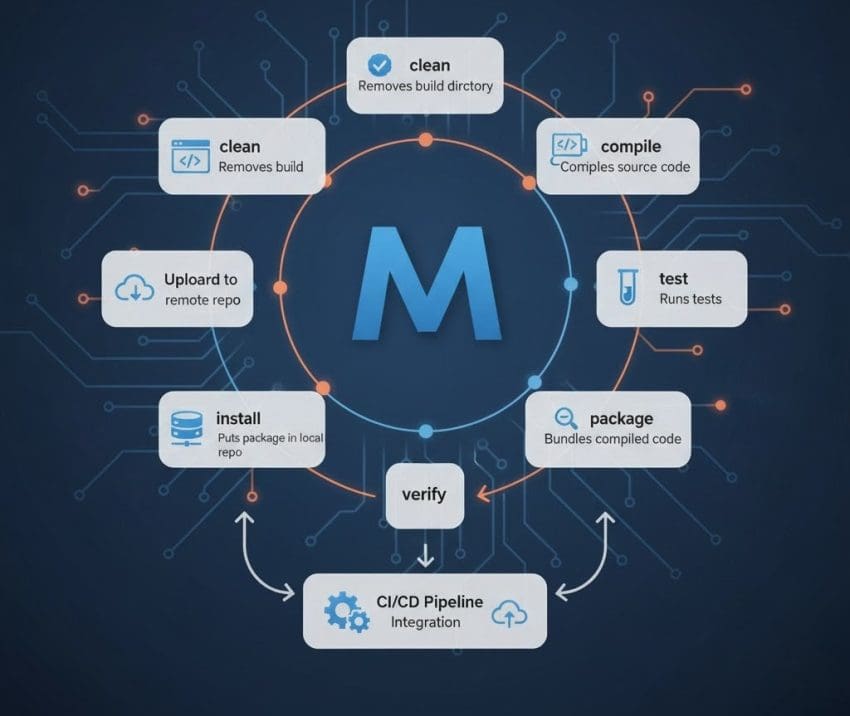
When working with Java-based applications, Maven stands out as one of the most widely used build automation and dependency management tools. It plays a central role in CI/CD pipelines — from compiling source code to packaging and deploying artifacts.
Here are five Maven build targets that are most commonly used in day-to-day DevOps activities.
1️⃣ mvn clean 🧹
Before starting a new build, it’s crucial to ensure no leftover artifacts exist from previous builds. The mvn clean command clears the /target directory, which typically holds all previously created .jar, .war, or other build artifacts.
Running this command ensures a clean slate before generating new builds, preventing any conflicts or unexpected behavior caused by stale files.
2️⃣ mvn compile ⚒️
The mvn compile command compiles all Java source files located under the src/main/java directory. These are the core source files written by developers.
This step converts the human-readable Java code into bytecode that can be executed by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). It’s one of the essential stages in every build lifecycle.
3️⃣ mvn test 🧪
Testing is an integral part of every CI/CD pipeline. The mvn test command executes all unit tests located in the src/test/java directory.
Running this target ensures that the code behaves as expected before it moves further in the deployment process. Automated testing helps catch issues early, improving overall build quality and stability.
4️⃣ mvn package 📦
Once the code is compiled and tested, it’s time to package it into distributable formats. The mvn package command packages the compiled code into a .jar, .war, or another format as defined in the pom.xml file.
This step creates the final artifact inside the /target directory, ready for deployment or distribution.
5️⃣ mvn install 🚀
Finally, the mvn install command installs the generated artifact into the local Maven repository, typically located in the .m2 directory. This allows the artifact to be reused in other local projects without rebuilding it every time.
Additionally, parameters can be passed to mvn install to push artifacts to remote repositories like JFrog Artifactory or Nexus Repository, ensuring they’re accessible across teams and environments.
🧠 Quick Recap
✔ mvn clean → Clears the target directory before a new build
✔ mvn compile → Compiles Java source files
✔ mvn test → Runs unit tests in the test directory
✔ mvn package → Packages the code into JAR/WAR files
✔ mvn install → Places the artifact into the local or remote repository
These five Maven build targets form the foundation of Java-based build pipelines. They ensure a smooth, structured process from cleaning up old artifacts to compiling, testing, packaging, and deploying the final output.
Whether it’s a local development environment or an automated CI/CD pipeline, these commands are essential building blocks for reliable software delivery.
To dive deeper… Check out these related topics: