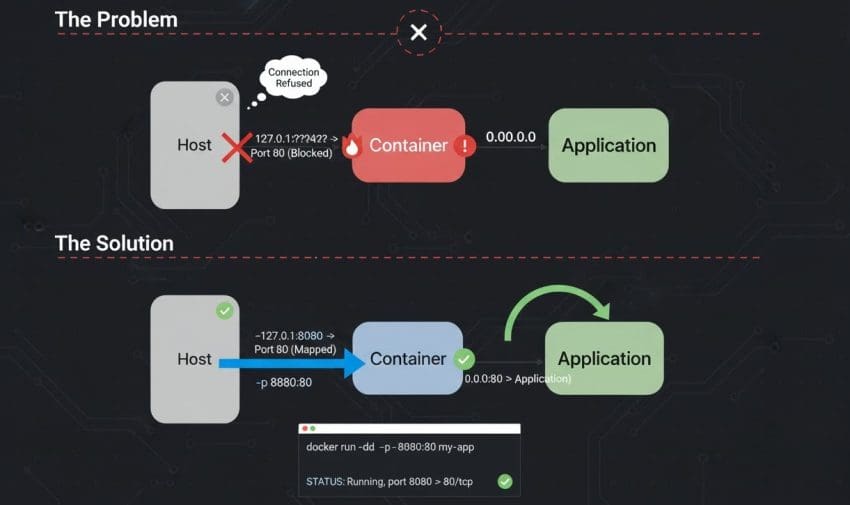
Sometimes an application inside a Docker container is running, but when accessed via localhost:<port>, nothing loads or it times out. This can be confusing because the container is running and port mapping has been configured, yet the application remains inaccessible from the host machine.
Example Scenario
- A container is started with:
docker run -p 8080:8080 myapp:latest- The application should be available on http://localhost:8080, but the browser shows nothing or times out.
Troubleshooting Steps
There are multiple reasons this can happen. Follow these steps to resolve the issue:
1. Recheck Port Mapping
✔ Confirm that the correct ports were used in the docker run command.
For example:
docker run -p 1100:8080 myapp:latest→ This maps container port 8080 to host port 1100. The application will then be available at http://localhost:1100.
2. Check if Port Is Already in Use
⭐ Ports like 80, 443, or 8080 are commonly used by other applications (e.g., web servers).
To check:
netstat -tulnp | grep 8080or
lsof -i :8080→ If the port is already taken, map the container to a different host port (e.g., -p 1100:8080).
3. Verify Firewall Settings
→ On some systems, a firewall may block incoming traffic.
✔ Temporarily disable or adjust firewall rules to allow traffic on the mapped port.
4. Application Binding Inside Container
⭐ Even if port mapping is correct, the application itself may only be listening on 127.0.0.1 inside the container.
Example (Flask app in Python):
app.run(host="127.0.0.1", port=8080)→ In this case, the application can only be accessed inside the container (curl localhost:8080).
✔ Fix: Bind the application to 0.0.0.0 so it listens on all interfaces:
app.run(host="0.0.0.0", port=8080)5. Inspect Logs and Container Details
⭐ If the issue still persists:
docker logs <container_id>
docker inspect <container_id>→ These commands provide insights into why the port might not be accessible.
Key Takeaways
- ✅ Containers may not be accessible on
localhostdue to wrong port mapping, port conflicts, firewall restrictions, or application binding issues. - ✅ Always confirm port mapping (
docker run -p host_port:container_port). - ✅ Ensure the application binds to
0.0.0.0instead of127.0.0.1. - ✅ Use logs and inspect commands for deeper troubleshooting.
By following these checks, applications running inside containers can be accessed smoothly from browsers or API clients without timeouts.
To dive deeper… Check out these related topics: